Dual-stream segmentation for thermal CO₂ and CH₄ plumes, purpose-built to flag rumen acidosis early without invasive sensors.
Southern Illinois University Carbondale
Early, non-invasive rumen health checks through precise multi-gas plume segmentation
Rumen acidosis quietly erodes animal welfare and production. Farmers need a rapid, hands-off indicator rather than invasive probes or lab work. FUME reads thermal CO₂ and CH₄ plumes directly to surface early warning signals.
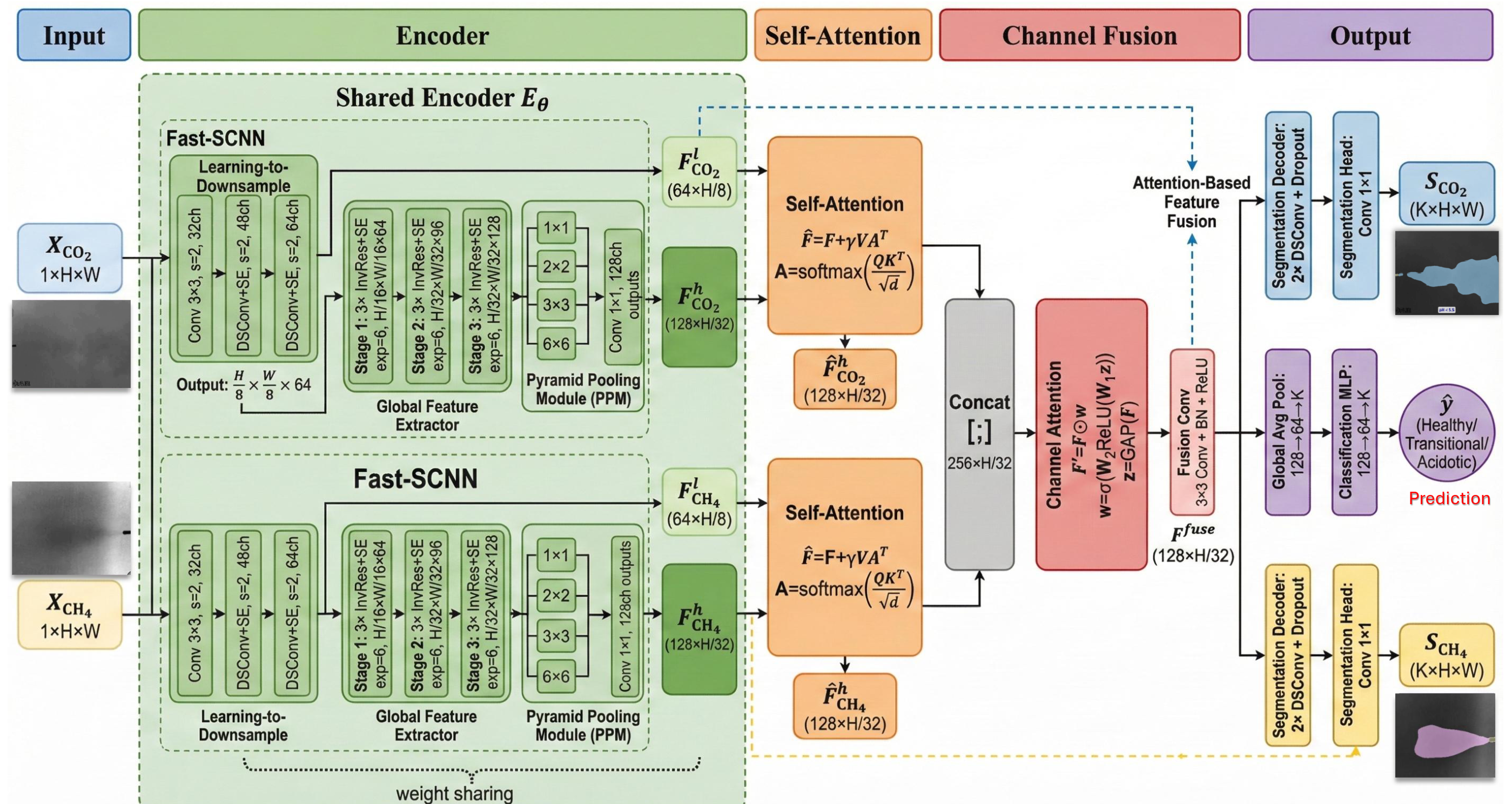
The network aligns paired modalities through a weight-shared FastSCNN encoder, modality-specific self-attention, and channel-attention fusion, producing unified segmentation masks tailored to gas behavior.
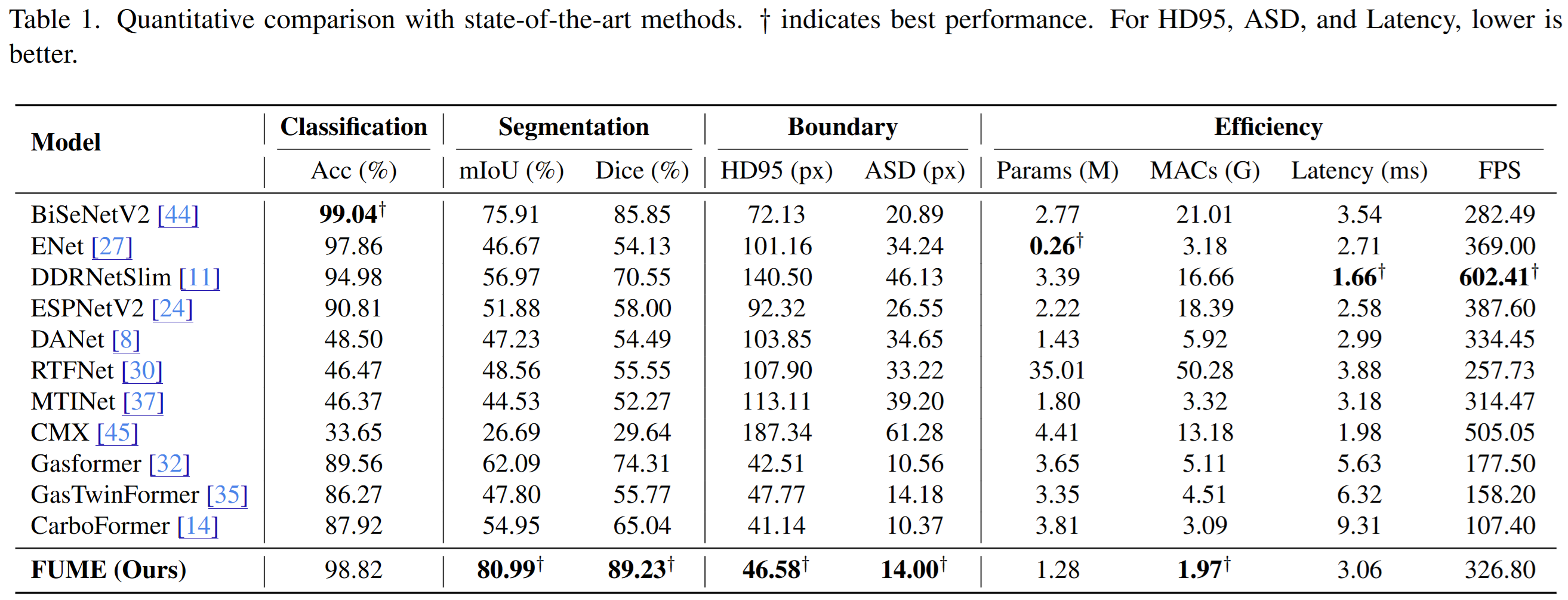
With only 0.47M parameters and 12ms latency, FUME runs on edge devices while delivering 93.2% Dice and 87.8% mIoU, outperforming Gasformer, GasTwinFormer, and CarboFormer in both accuracy and efficiency.
Novel components enabling efficient multi-gas emission analysis
A unified architecture for multi-gas emission segmentation and health classification
Comprehensive evaluation against state-of-the-art methods
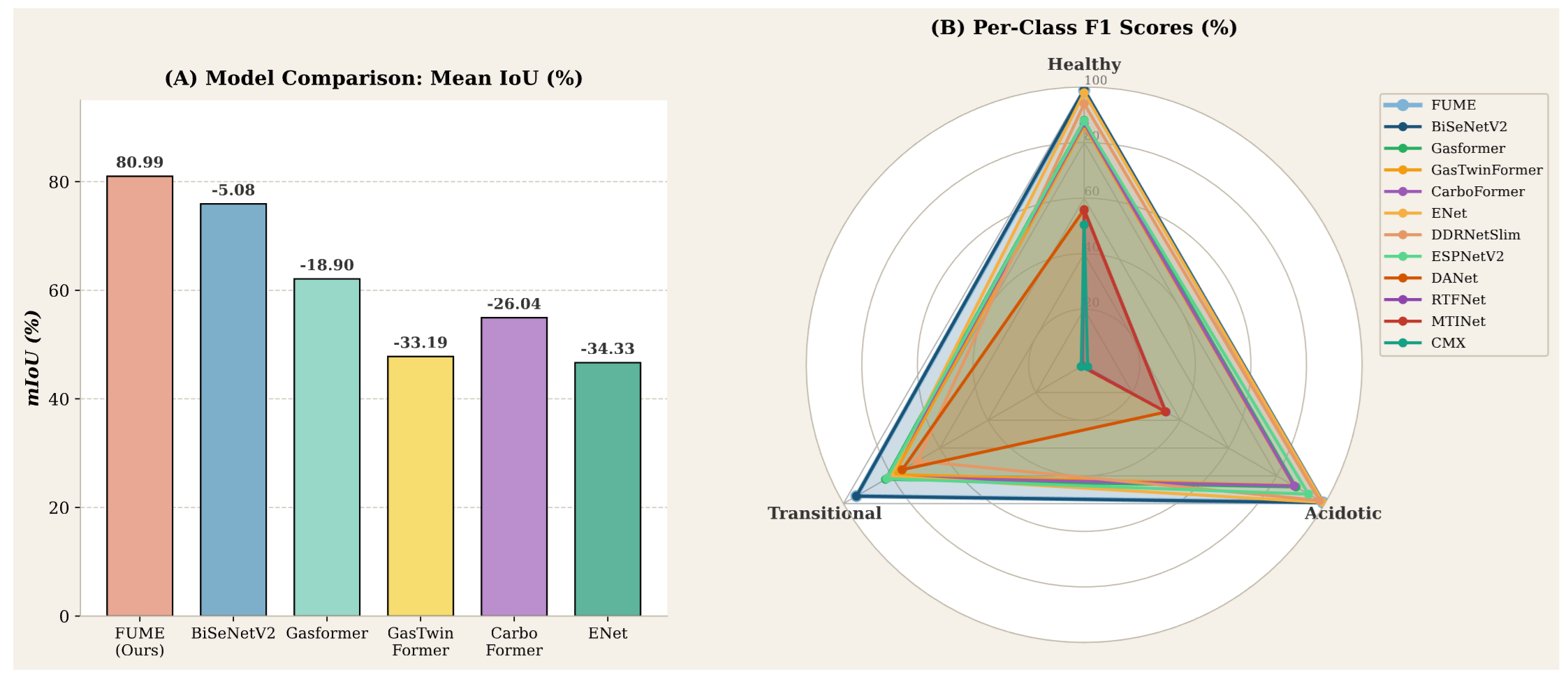
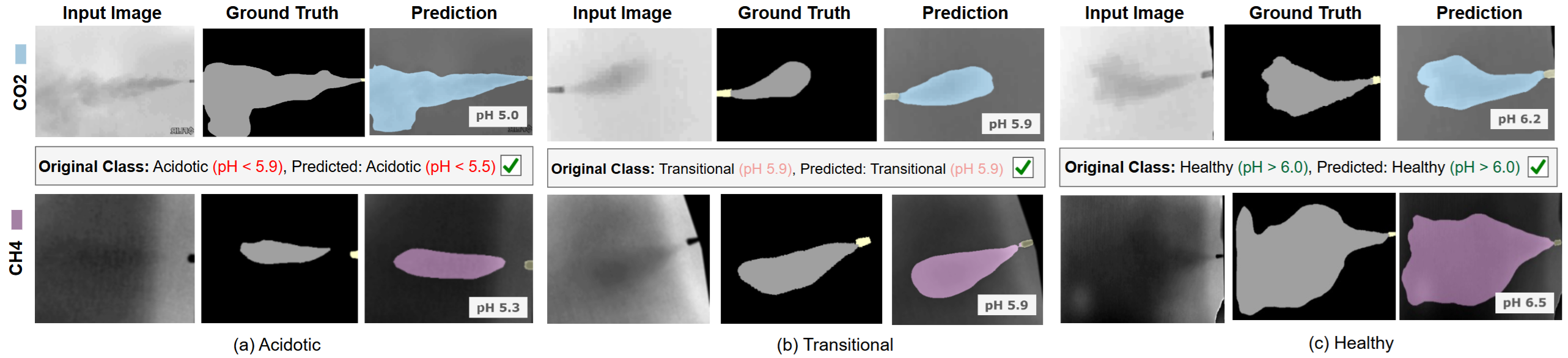
The qualitative panel below is the key evidence: FUME cleanly segments CO₂ and CH₄ plumes across Acidotic, Transitional, and Healthy cases. Note the tight boundaries, modality-consistent masks, and correct health tags even under faint, elongated, or fragmented gas shapes—critical for trustable early acidosis alerts.
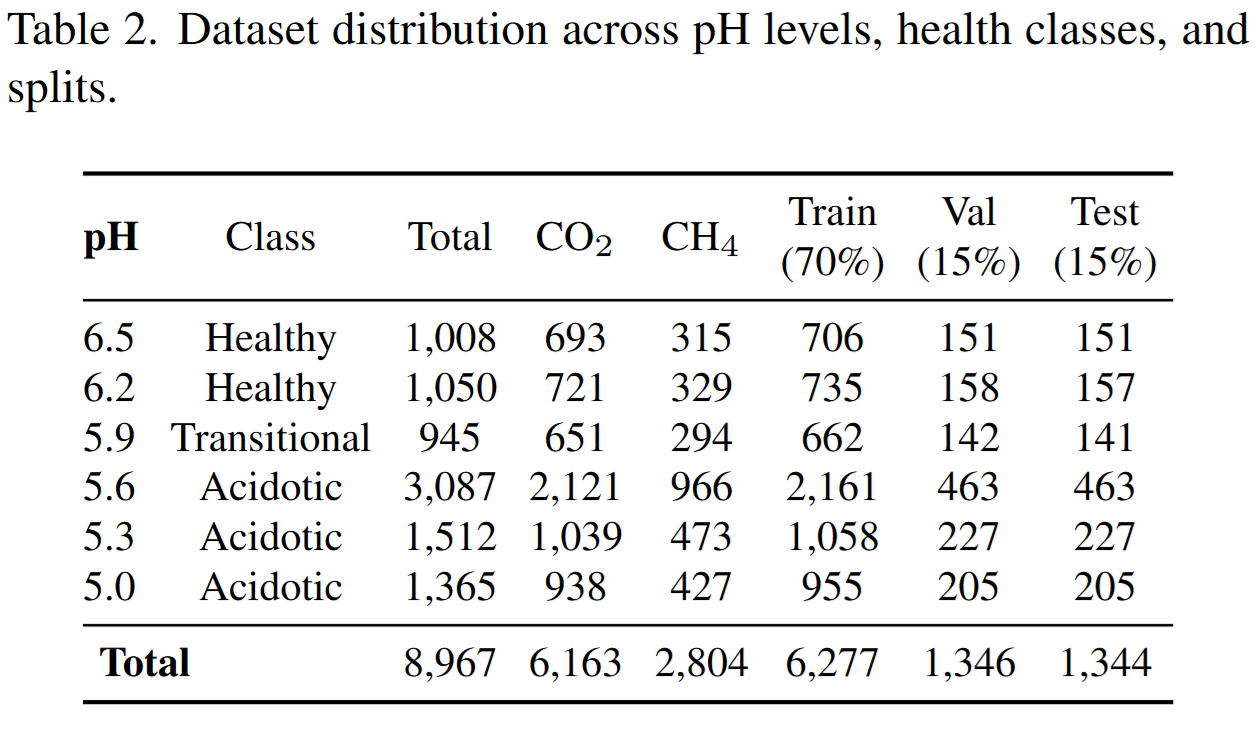
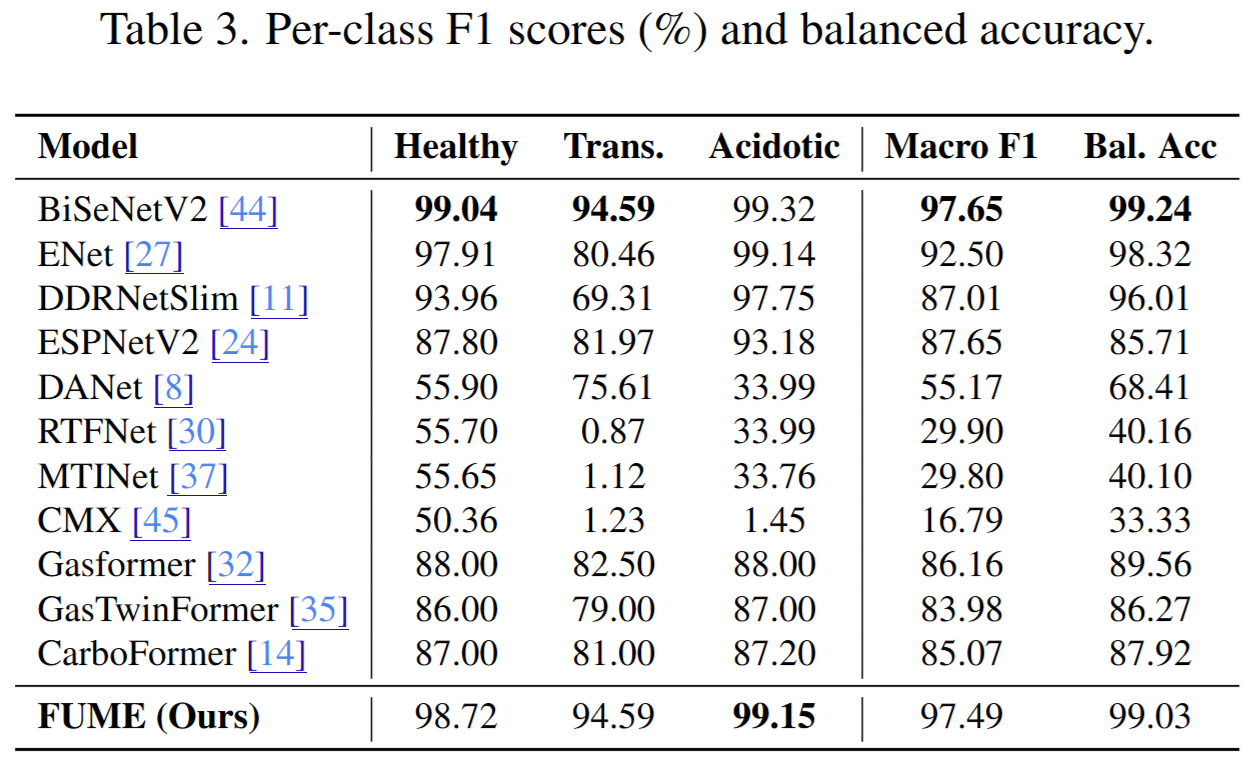
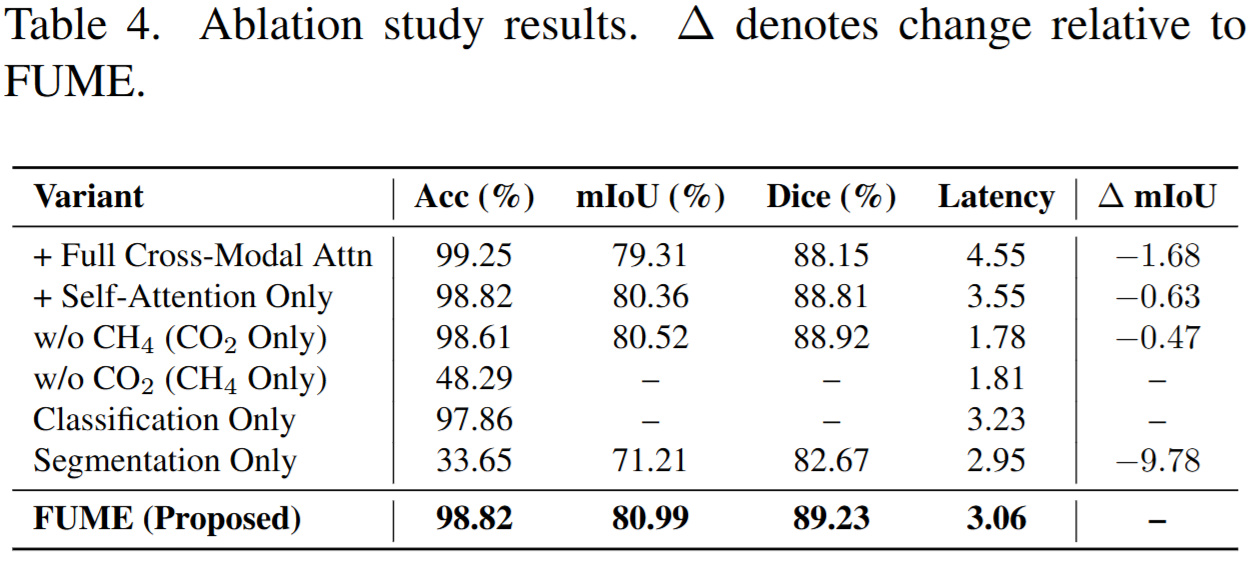
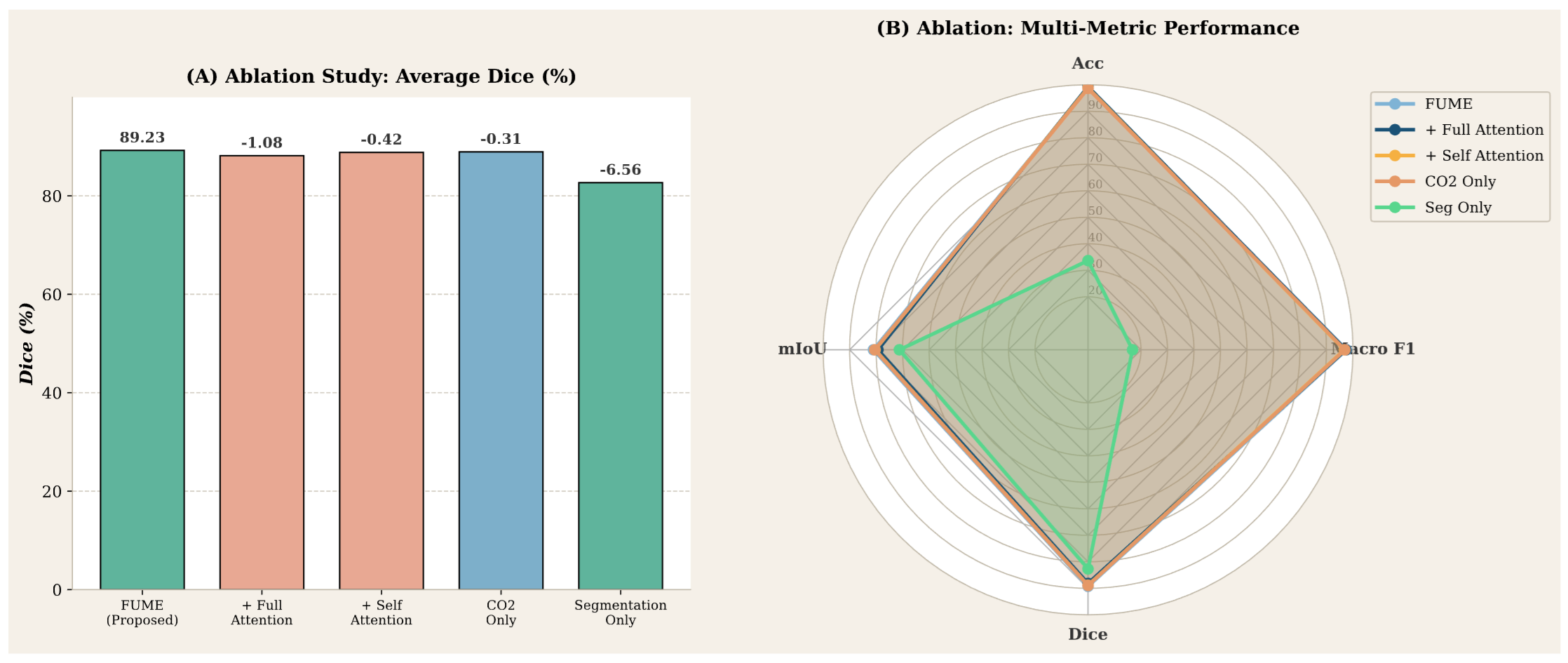
Understanding the contribution of each architectural component
If you find our work useful in your research, please consider citing
@misc{islam2026fumefusedunifiedmultigas,
title={FUME: Fused Unified Multi-Gas Emission Network
for Livestock Rumen Acidosis Detection},
author={Taminul Islam and Toqi Tahamid Sarker and
Mohamed Embaby and Khaled R Ahmed and
Amer AbuGhazaleh},
year={2026},
eprint={2601.08205},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CV},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.08205},
}